What is Green House Effect? with Example - Explore Study
The greenhouse effect increases the temperature of the Earth by trapping heat in our atmosphere. This keeps the temperature of the Earth higher than it would be if direct heating by the Sun was the only source of warming.When sunlight reaches the surface of the Earth, some of it is absorbed which warms the ground and some bounces back to space as heat. Greenhouse gases that are in the atmosphere absorb and then redirect some of this heat back towards the Earth.
What is Green House Effect?
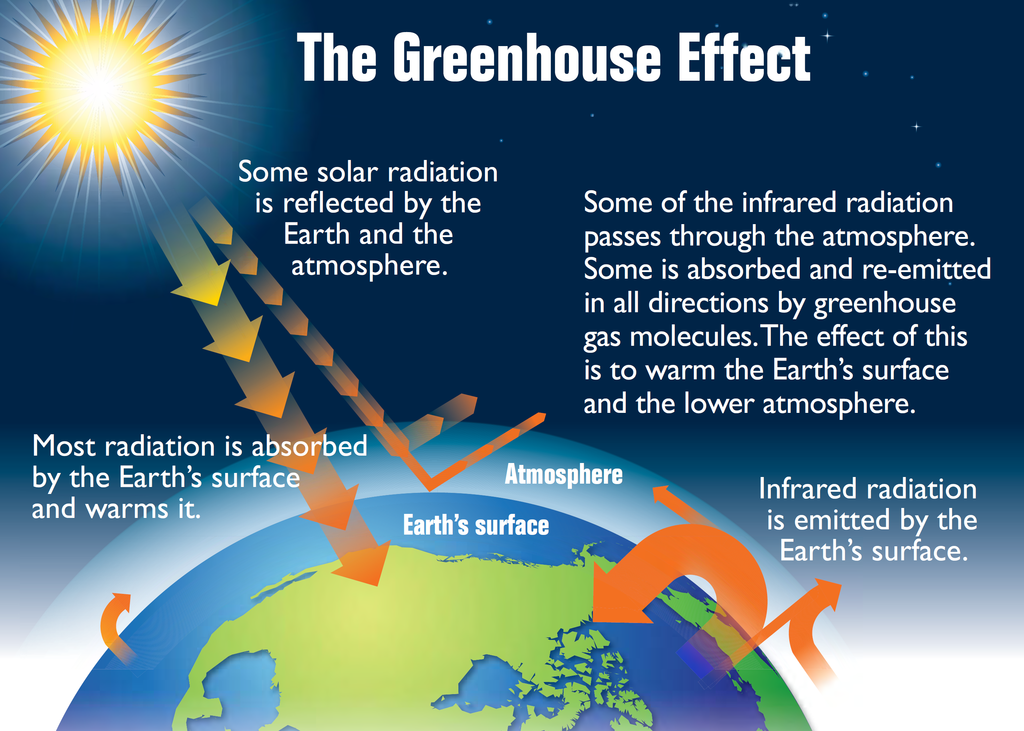
The greenhouse effect is a major factor in keeping the Earth warm because it keeps some of the planet's heat that would otherwise escape from the atmosphere out to space. In fact, without the greenhouse effect the Earth's average global temperature would be much colder and life on Earth as we know it would not be possible. The difference between the Earth's actual average temperature 14° C (57.2° F) and the expected effective temperature just with the Sun's radiation -19° C (-2.2° F) gives us the strength of the greenhouse effect, which is 33° C.
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that is millions of years old. It plays a critical role in regulating the overall temperature of the Earth. The greenhouse effect was first discovered by Joseph Fourier in 1827, experimentally verified by John Tyndall in 1861, and quantified by Svante Arrhenius in 1896.
How does the greenhouse effect work?
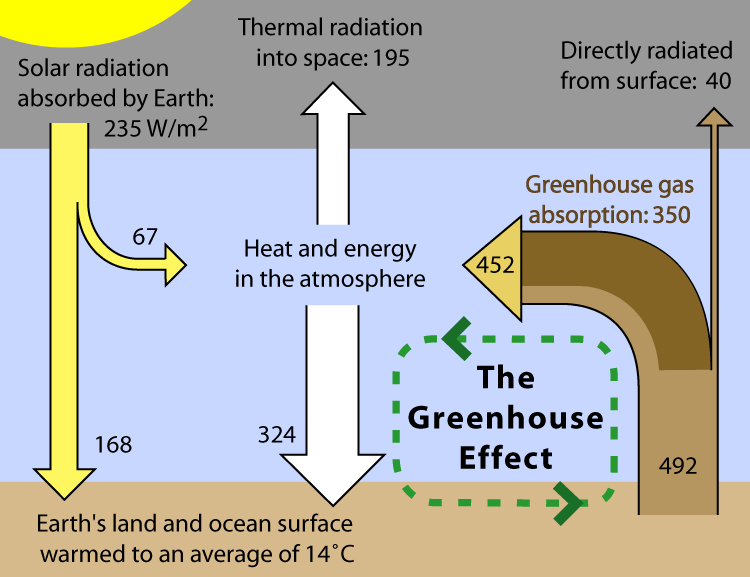
To understand exactly how the greenhouse effect works, imagine the following: a warm, sunny day where the sun shines bright on the Earth. This sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes into the planet's atmosphere and warms the Earth. Part of this energy is absorbed by the Earth's surface, transformed into heat (long wave radiation) and radiated back towards space. But as this heat goes up through the atmosphere, some of it is trapped by the different greenhouse gases and doesn't escape into space. This in turn warms up the Earth's atmosphere; just like the windows of a greenhouse that lets light in and keeps the heat within to warm the plants growing inside.
Since some of the heat can't escape into space, it continues to add up which then warms up the Earth. This is what we call the greenhouse effect. So the more greenhouse gases you have in the atmosphere, the more heat stays on Earth.
If the amount of energy from the sun and the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere remain the same, then the average temperature on Earth will also be constant. But this is no longer the case. The amount of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere is the highest it has been in the last 3 million years. This is enhancing the greenhouse effect and making the Earth warmer than normal, which is affecting the planet's weather patterns, creating global warming and climate change.
An everyday example of the greenhouse effect
If you open the door of a car that has been left parked in the sun for a couple of hours, you'll notice that the temperature inside the car is much warmer than the temperature outside. This is because the windows of the car allow the sunlight to enter. This light, once inside, is then partially converted into heat. However, these same windows do not allow the heat inside the car to pass through as easily as light, so some of this heat accumulates. The net effect is that more heat remains in than can come out, increasing the temperature inside the car.

Comments
Post a Comment